读医学网
骨盆骨折分类及治疗指南(四)
发布时间:2014-05-20 09:24 类别:呼吸系统疾病 标签:损伤 神经 骨折 骶骨 来源:互联网
13. Complex fractures
13. 复杂骨折
Not uncommonly, pelvic fractures may display features of more than one pattern of injury but the same rules of stability apply.
并不罕见,骨盆骨折的特征表现出可能不止一种损伤类型,但适用同样的稳定性原则。
14. Sacral fractures
14. 骶骨骨折
Commonly overlooked, sacral fractures should be considered as part of the pelvic ring. Notoriously dif?cult to visualise on plain radiography, these fractures have a high association of potentially devastating neurological injury and should not be missed. Depending on the exact site of fracture, the rate of complication differs greatly.
常被忽视,骶骨骨折应被视作骨盆环的一部分。众所周知,由于该骨折难以在平片上显示,潜在性地与毁灭性神经损伤高度相关,因此不应漏诊。由于取决于骨折的确切位置,并发症的发生率差别很大。
A classi?cation system has been devised to help predict the risk of neurological impairment [23]:
Zone 1: Involving the sacral ala lateral to sacral foramina. This can cause L5 nerve root impingement, with approximately 6% sustaining neurological injury [23].
Zone 2: Involving the neuro foramina which can cause unilateral sacral anaesthesia. No involvement of the central sacral canal.
Zone 3: Involving the body of sacrum. This injury has a high association with neurological compromise (approx. 56% [23]), and may result in cauda equina syndrome.
一种分类系统被设计用来协助预测神经损伤的风险[23]:
1区:包括骶骨翼侧至骶孔。可引起L5神经根损失,大约6%将遗留神经损伤后遗症。
2区:包括神经孔,引起单一骶区感觉缺失。不包括中央骶管。
3区:包括骶骨体。此处损伤与神经损伤高度相关(大约56%[23]),可引起马尾综合征。
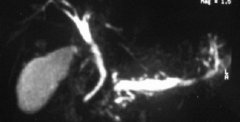
Transverse fractures are less common, but can also result from high energy trauma. Transverse fractures above S4 have a high rate of associated neurological injury, whereas the risk below this level is low. These fractures can cause intraspinal and intraforaminal nerve root compromise (Fig. 7a and b).
横行折不常见,但可由高能创伤引起。S4以上横行折合并神经损伤几率高,而此节段以下神经损伤风险低。此型骨折可引起椎管内和骶孔内神经根损伤(图. 7a and b)。


图7:(a 和 b)男性,酒后坐下过猛致骶骨骨折。此种低能损伤机制增加了对潜在骨质减少的关注。这种骨折在前后位平片上难以发现,但这种特殊的损伤在侧位片上更明显(b, 箭头所示)。
下一篇:新耶鲁方案可使ICU患者血糖达标 上一篇:IDSA发布首个MRSA感染治疗指南
- 猜你会喜欢....